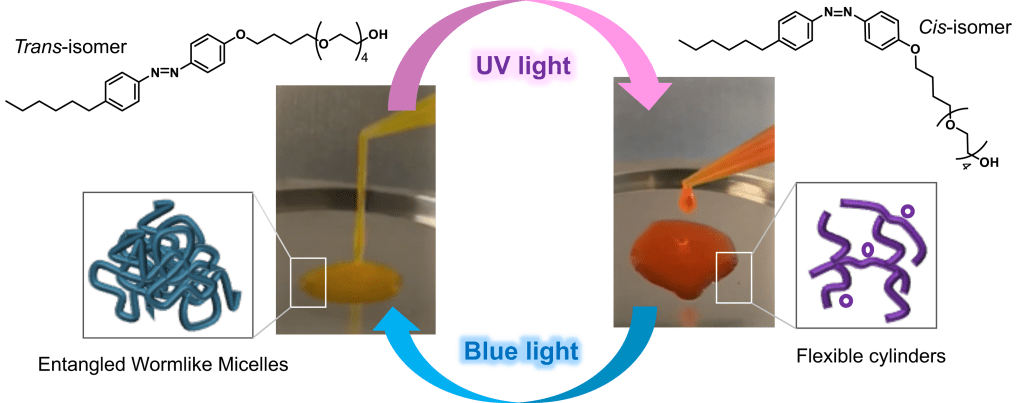
Congratulations to former and current group members Camille, Judith and Elaine for their paper “Light-Responsive Self-Assembly of a Cationic Azobenzene Surfactant at High Concentration” which has just been accepted by Soft Matter.
They report the high-concentration and lyotropic liquid crystalline behaviour of trimethylammonium bromide azobenzene photosurfactants for the first time. These surfactants are often used in a variety of applications (DNA compaction, photofoaming, microfluidics) and have been studied at low concentration, but reports of their formation of lyotropic liquid crystals remain rare.
Using polarised optical microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering, self-assembled structures with long-range order and optical anisotropy are found for the trans-isomer. These structures are lost or disrupted with UV light irradiation and photoisomerisation to the cis-isomer.
The work was carried out using X-ray beamtime at Diamond Light Source.